Accounting Equation Formula
This ratio measures a firm’s liquidity – whether it has enough resources (current assets) to pay its current liabilities. It calculates how many dollars in current assets are available for each dollar in short-term debt. Assets are also classified on the balance sheet as either current assets or long-term assets. A current asset, such as an account receivable or marketable security, is expected to be liquidated within one year. A long-term asset, such as a fixed asset, is expected to be liquidated in more than one year.
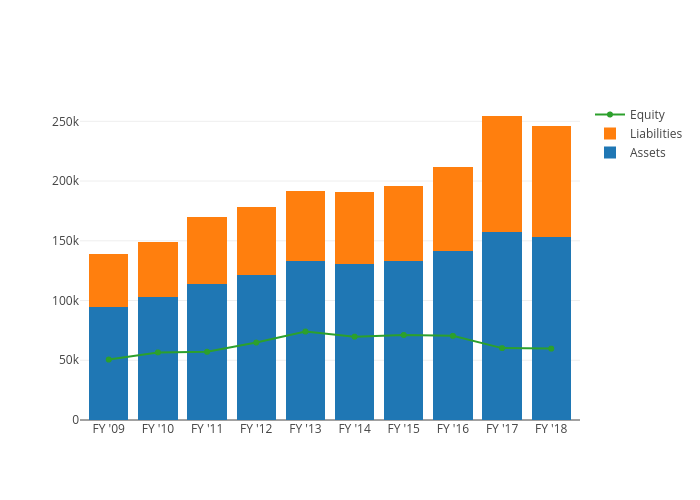
Learning From The Equation
Like income, expenses are also measured every period and then closed as part of capital. Current-portion of a long-term liability – the portion of a long-term borrowing that is currently due.
Cash Flow Vs. Balance Sheet
Abalance sheetreports a company’s assets, liabilities, andshareholders’ equityfor a specific period. The balance sheet shows what a company owns and owes, as well as the amount invested by shareholders. Revenue is only increased when receivables cash basis are converted into cash inflows through the collection. Revenue represents the total income of a company before deducting expenses. Companies looking to increase profits want to increase their receivables by selling their goods or services.
How Do The Balance Sheet And Cash Flow Statement Differ?
Return on invested capital gives a sense of how well a company is using its money to generate returns. Fixed assets have a useful life of over one year, while current assets are expected to be liquidated within one fiscal year or one operating cycle. The four major types of capital include debt, equity, trading, and working capital. It is usually difficult to determine the value of intangible assets.
Reading The Balance Sheet
The assets on the balance sheet consist of what a company owns or will receive in the future and which are measurable. Liabilities are what a company owes, such as taxes, payables, salaries, and debt. The shareholders’ equity section displays the company’s retained earnings and the capital that has been contributed by shareholders.
Why assets is equal to liabilities?
Any increase in liabilities is a source of funding and so represents a cash inflow: Increases in accounts payable means a company purchased goods on credit, conserving its cash. Decreases in accounts payable imply that a company has paid back what it owes to suppliers.
Separating current liabilities from long-term liabilities like loans and other long-term debt allows business owners to more effectively plan for short-term obligations. These cash amounts are usually followed by assets that the company is owed, but bookkeeping are not in their possession yet. Thinkaccounts receivablewhere outstandinginvoicesand payments will translate to cash in the coming months. As a rule of thumb, any assets that could be turned into cash within a year are considered current assets.
- Personal net worth is the difference between an individual’s total assets and total liabilities.
- However, the payments due on the long-term loans in the current fiscal year could be considered current liabilities if the amounts were material.
- Bonds, mortgages and loans that are payable over a term exceeding one year would be fixed liabilities or long-term liabilities.
Noncurrent assets are a company’s long-term investments, which are not easily converted to cash or are not expected to become cash within a year. Although capital investment is typically used for long-term assets, some companies use it to finance working capital. Current asset capital investment decisions what are retained earnings are short-term funding decisions essential to a firm’s day-to-day operations. Current assets are essential to the ongoing operation of a company to ensure it covers recurring expenses. Capital investment decisions are long-term funding decisions that involve capital assets such as fixed assets.

Take the assets you listed in step one and plug them into the template, making sure to group them into categories like current assets, fixed assets and other assets. Finally, calculate the value of intangible assets—non-physical assets of financial value like a business’s reputation. This article has more information on intangible assets and how to calculate them. Then move on to listing the value of fixed assets (assets that are harder to convert into cash) like buildings and machinery. Find the value of long-term investments like stocks and bonds, too.
Most companies will have these two line items on their balance sheet, as they are part of ongoing current and long-term operations. Accrued expenses are listed in the current liabilities assets = liabilities + equity section of the balance sheet because they represent short-term financial obligations. Companies typically will use their short-term assets or current assets such as cash to pay them.

Government organizations do not generally follow standards established for individuals or businesses. Tara Kimball is a former accounting professional with http://1018.lv/2019/10/10/accounting-discussion-questions-chapter-3-4/ more than 10 years of experience in corporate finance and small business accounting. An error in journal entries could cause an unbalanced balance sheet.
The issuing company creates these instruments for the express purpose of raising funds to further finance business activities and expansion. Your liabilities are any debts your company has, whether it’s bank loans, mortgages, unpaid bills, IOUs, or any other sum of money that you owe someone else. In accounting and bookkeeping, the term liability refers to a company’s obligation arising from a past transaction. Notes payable are the amounts still owed on any long-term debts that won’t be repaid during the current fiscal year. “Total long-term assets” is the sum of capital and plant, investments, and miscellaneous assets.
A higher proportion of assets compared to shareholder equity demonstrates the extent to which debt (leverage) is used in a company’s capital structure. But if that company takes on financial leverage, its ROE would rise above its ROA. By taking on debt, a company increases its assets thanks to the cash that comes in. But since shareholder equity equals assets minus total debt, a company decreases its equity by increasing debt.
A liability is something a person or company owes, usually a sum of money. Liabilities are settled over time through the transfer of economic benefits including money, goods, or services. Recorded on the right side of the balance sheet, liabilities include loans, accounts payable, mortgages, deferred revenues, earned premiums, unearned premiums, and accrued expenses. Current assets are short-term assets, whereas fixed assets are typically long-term assets.
What if assets are more than liabilities?
a debt is a liability to the person who owes a debt and is an asset to the person who’s being owed money. According to International Financial Reporting Framework, essentially, you have a liability if you have an obligation to someone and you have an asset if you receive an economic benefit of something.
Shareholders’ equity is a company’s total assets minus its total liabilities. Shareholders’ equity represents the amount of money that would be returned to shareholders if all of the assets were liquidated and all of the company’s debt was paid off.
As you will see, it starts with current assets, then non-current assets and total assets. Below that is liabilities and stockholders’ equity which includes current liabilities, non-current liabilities, and finally shareholders’ equity. Every company must report their total asset value following the same standards as developed by generally accepting accounting periods, regardless of company size or classes of assets on hand. To comply with the basic accounting equation, total assets must equal the sum of total liabilities and total stockholders’ equity combined.
Financial statements include the balance sheet, income statement, and cash flow statement. Your business’s revenues and expenses are also recorded in capital accounts because they relate to how much money your company makes over a period of time. At the end of each accounting cycle, a business’ profits get transferred to a capital account. The income and retained earnings of the accounting equation is also an essential component in computing, understanding, and analyzing a firm’s income statement.






0 responses on "How To Review An Unbalanced Balance Sheet"